I think I have chest symptoms
Chest pain

● What would the pain feel like?
If your chest pain feels like it is in the entire chest area, and/or burning, and/or tightening, and/or discomforting, and these feelings disappear within 10 minutes, then it is highly likely it is angina. If these feelings continue for more than 30 minutes, then it could be a myocardial infarction.
● Where do I feel the pain?
You might feel your pain in the chest, but it is not limited to the chest area. The pain might also be on your back, left shoulder, jaw and teeth, or pit of the stomach.
● What tests are there to check my chest pain symptoms?
Blood work, ECG, echocardiogram, CT angiography, cardiac catheterization.
Find a cardio-endovascular specialist
Palpitations, dizziness, syncope

● What would palpitation feel like?
Skipped heart beat
This could be premature contraction, which is a type of arrhythmia. Some premature contractions do not require treatment, while there are others that can be life threatening.
Fast heart beat: fluttering
Tests need to be run to identify what type of arrhythmia this is, as it could be something requiring treatment.
Strong heart beat: pounding
This could be non-cardiac origin; for examples, anemia, thyroid hormones, stress can bring about the pounding feeling in your heart.
● What would cause dizziness and syncope?
Abnormally rapid or slow pulse can shorten the supply of blood to the brain, causing you to faint or feel dizzy.
● What tests are there to check my palpitation and dizziness?
Blood work, 24-hr ECG, echocardiogram, intracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS).
Find an arrhythmia and heart failure specialist
Shortness of breath, swelling, fatigue

Shortness of breath, swelling, fatigue could be indications of valvular disease or heart failure. To identify the causes to your symptoms, the following examinations are performed.
Blood work, urinalysis, ECG, echocardiogram, chest X-ray.
We will assign you a specialist based on your symptoms. Please contact us for an appointment.
Working of the heart
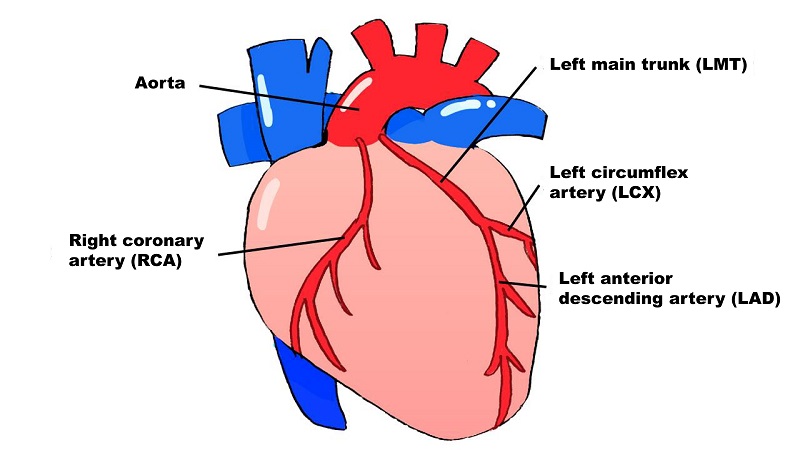
The heart is a pump that sends blood throughout the body, and that pumping movement is regulated by electric signals, automating its contraction and expansion. On the surface of the heart are three major coronary arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart.
Cardiac diseases
● Ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease is a disease in which the blood vessels around the heart become narrowed or blocked, causing the heart function to deteriorate. Ischemic heart disease can be divided into two main categories, angina pectoris and myocardial infarction.
Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris is a condition in which the heart arteries become narrowed from atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient supply of blood to the heart.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is a condition in which the heart arteries are so severely narrowed or blocked that blood flow is significantly reduced or completely interrupted resulting in part of the heart being necrotic (dead and immobile).
● Valvular disease
The heart has four valves to maintain blood flow in one direction and to also prevent it from flowing backward. When the valve(s) fails to function properly, it is a condition called valvular disease. Heart valve disease can be divided into two categories, stenosis and insufficiency. Stenosis is when heart valve becomes hardened, making it difficult to flap open; whereas insufficiency is when heart valve fails to close properly and blood leaks backward.
● Aortic disease
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the body; it is an important blood vessel in that it transports blood out of the heart. Aortic disease is caused by degeneration of blood vessels from arteriosclerosis or hypertension, resulting in the formation of aneurysm or tear in the aorta. Aortic disease can be fatal if it is not treated in time.
● Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a disease in which electric signals to move the heart in a consistent rhythm for some reason becomes abnormal, causing the heart rhythm to be irregular. Depending on the type of arrhythmia, syncope may occur.
● Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart’s function is severely impaired, resulting in shortness of breath and swelling. As symptoms worsen over time, lifespan is shortened as well. Heart-related diseases are the cause to heart failure, and depending on the cause, treatment varies.
Treatment
● Ischemic heart disease
Treatment for ischemic heart disease is mainly by medication and/or catheterization to control symptoms and prevent recurrence. However, it is just as important after treatment to pay attention to your lifestyle.
● Valvular disease
Treatment for valvular disease becomes necessary when the condition of the valve deteriorates; if left untreated, the heart will gradually lose its ability to function properly.
● Aortic disease
Depending on the size of the aneurysm, patient might be able to go without surgery and can be monitored through medication and improvement of lifestyle. However, large aneurysm at risk of fatal rupture requires surgical procedure to treat.
Aortic dissection varies greatly depending on the location of the dissection. If the dissection is in the ascending aorta, emergency surgery is required; if the dissection is not in the ascending aorta, then in principle treatment is focused on reducing blood pressure and relieving pain. However, if there is rupture or impeded blood circulation, then emergency surgery is necessary.
● Arrhythmia
There are many types of arrhythmia, and depending on the type of arrhythmia, treatment differs. Tests are run before your doctor determines the appropriate course of treatment–be it monitoring via oral medication, catheter ablation, or implantation of a pacemaker. In some cases, arrhythmia is caused by clogged blood vessels around the heart, if that is the case, cardiac catheterization is performed.