What is arrhythmia?
Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
The most severe forms of prognostic symptom in cerebral infarction is that of cardiogenic cerebral embolism caused by atrial fibrillation. This type of arrhythmia increases with age, and expects to affect over 1 million people in Japan by 2030. The aims of treatment are to (1) control complications, (2) prevent cerebral infarction through anti-coagulant treatment (medication to prevent blood from coagulating), and (3) prevent Afib from becoming chronic by maintaining regular pulse.
Though there are anti-arrhythmia medications to treat arrhythmia, they might not work for some patients, and some patients cannot take them because of the side effects. Non-pharmaceutic treatment would then involves catheter ablation. In recent years, innovative technology along with 3D mapping have become mainstream, making treatment more effective and safe. The latest report shows that catheter ablation is effective toward reducing chronic Afib by 10%. For that matter, many medical facilities are performing catheter ablation for Afib before it becomes chronic.
There was no effective method to prevent Afib from becoming chronic in the past. However, it is now possible to prevent chronic Afib and maintain normal pulse with one single or multiple procedures.
● Assessing Left Atrial Thrombosis (Transesophageal Echocardiography)
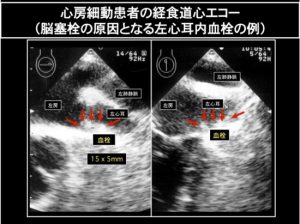
In Afib cases, blood flow is staggered inside the heart cavity, causing blood clots to form inside the left atrial appendage. If this blood clot breaks off within the heart chamber, it will pass through blood vessels and travel to the brain. If this blood clot clogs up a brain vessel, cerebral embolism occurs, resulting in cerebral infarction that could leave damaging after affects. Regardless of whether the Afib is symptomatic, paroxysmal, or persistent, it can cause cerebral infarction. To prevent blood clot from forming, it is necessary to be on appropriate anti-coagulant drugs. However, in some patients, even with the use of anti-coagulants, blood clots still form. For these patients, as well as high risk patients such as seniors, diabetic patients, patients with past history of cerebral infarction and valvular disease patients, performing Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) to assess blood clot is absolutely necessary.
- Regardless of whether your Afib is symptomatic, paroxysmal, or persistent, it can cause cerebral infarction.
- TEE is an effective exam for diagnosing intracardiac thrombosis associated with Afib.
- Patients who had cerebral infarction of unknown cause or valvular disease (especially of mitral valve) are recommended to receive TEE to assess left atrial thrombosis.
● Balloon Treatments for Afib
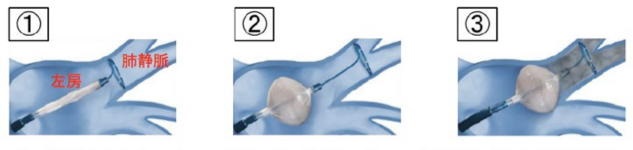
- Cryo-balloon

Makiminato Chuo Hospital introduced the use of cryo-balloon in 2016 and endoscopic laser balloon catheterization in 2018 for treatment of Afib. Catheter used in cryo-balloon ablation has a diameter of 28mm. The treatment involves pressing the balloon at the entrance of the pulmonary vein to freeze the left atrial myocardium at -50 degrees, thus isolating the electrical current of the pulmonary vein. Compared to traditional high frequency ablation which takes 5 to 10 minutes to work on one pulmonary vein, cryo-ablation takes only 3 minutes to complete. Another merit of cryo-ablation is lower risk of blood clot formation. One of the disadvantages of cryo-ablation is that it is limited to pulmonary veins. Since 10 to 30% of Afib occurs outside of pulmonary veins, for these cases, high frequency ablation must also be included during treatment. Another disadvantage of cryo-ablation is there is approximately 10% of the cases who developed phrenic nerve palsy.
- Laser-balloon
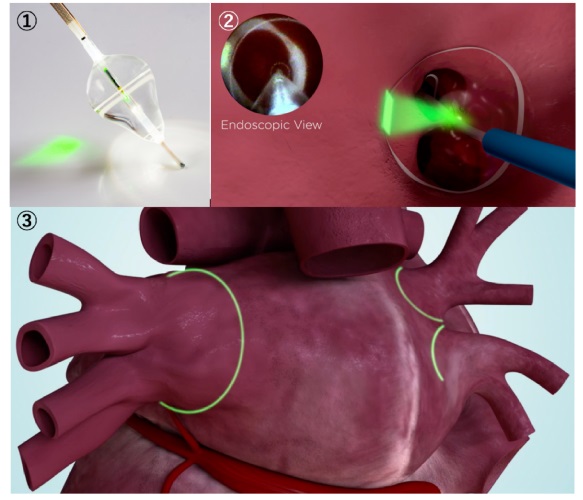
In laser-balloon, the treatment involves pressing the balloon at the entrance of the pulmonary vein, and under the guidance of an endoscope applies laser in a circle to isolate the electrical current of the pulmonary vein. Compared to traditional high frequency ablation, this method allows continuous and consistent cauterizing. Unlike cryo-balloon, laser-balloon is size-adjustable, giving it the freedom to target different formations of pulmonary veins. Since 10 to 30% of Afib occurs outside of pulmonary veins, for these cases, high frequency ablation must also be included during treatment.
Merits of cryo- and laser-balloon procedures
- Effective treatment leaving no scars (discharged in 1 to 2 days after procedure).
- Effective in preventing Afib from becoming chronic.
- Cryo-balloon (freezing) shortens procedure time.
- Laser-balloon allows continuous and consistent cauterizing.
● Tailor-made Treatment for Afib via 3D Mapping
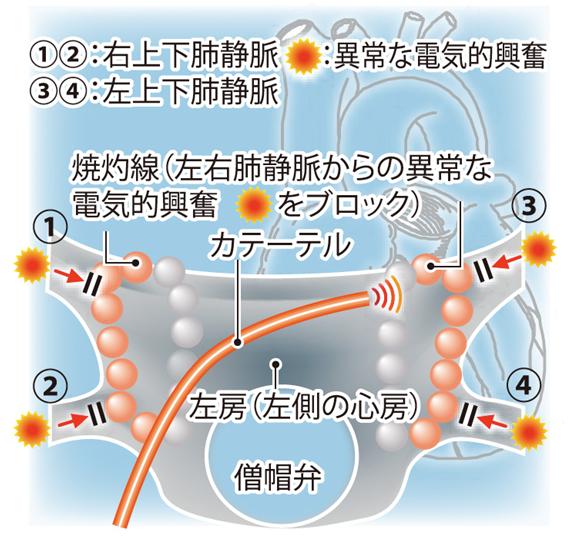
Image to the right shows isolation to both right and left pulmonary veins. Pulmonary veins (blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the heart) are the main locations where Afib occurs. Circular ablations creating a cauterizing line to each of the left and right pulmonary veins isolate the electrical path to the left atrium.
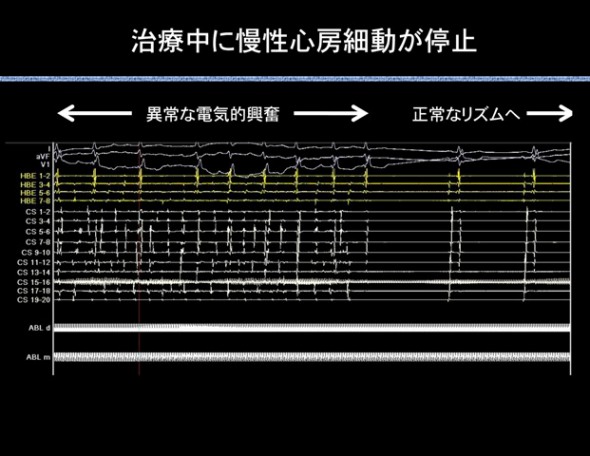
However, for chronic Afib, isolating the pulmonary veins alone usually is not effective. For these patients, we use the tailor-made approach to catheter ablation. The above case shows the abrupt termination of chronic Afib to normal heartbeat.
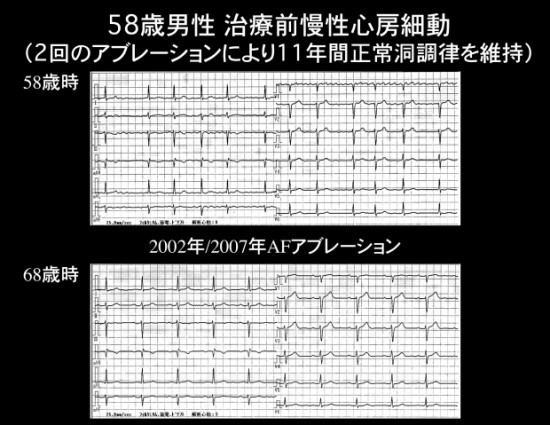
To control atrial fibrillation and maintain a normal heartbeat over an extended period of time, multiple catheter ablation may be required. The case to the right received a second catheter ablation and was able to maintain normal heartbeat for more than 11 years.
Merits of tailor-made approach
- Effective treatment leaving no scars (discharged in 1 to 2 days after procedure).
- Effective in preventing Afib from becoming chronic.
- Effective treatment for normalizing chronic Afib.
Refractory Tachycardia
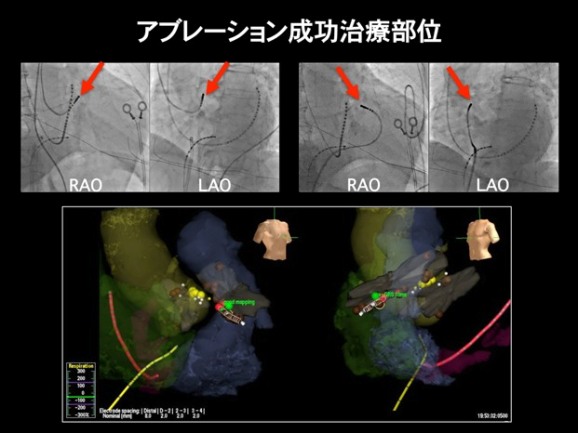
Below is a case who came to our arrhythmia outpatient clinic with cerebral ischemic symptoms such as non-vertigo and feeling of blacking out. ECG was ordered and revealed frequent ventricular tachycardia (VT). The patient underwent catheter ablation using high density 3D mapping system. VT disappeared with one treatment and the patient was able to maintain normal heartbeat without needs of medication.
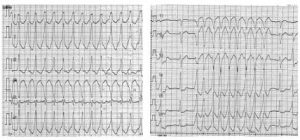
Merits of high density 3D mapping for definitive treatment of refractory tachycardia
- Effective treatment leaving no scars (discharged in 1 to 2 days after procedure).
- Effective one-time definitive treatment for different types of tachycardia.
- Has longer lasting effect and is more definitive than drug therapy.
Mitral Valve Stenosis
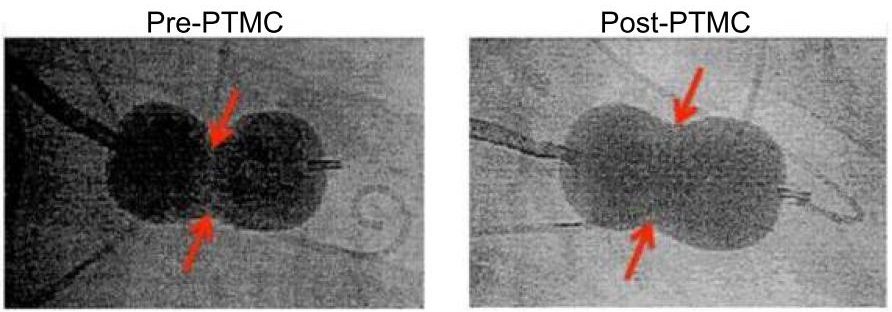
There are four valves inside the heart, and mitral valve is one of them. Prognostic loss of mobility to the valve from inflammation results in progressive stenosis, obstructing blood passage and causing patient to feel tired and out of breath during exertion. In severe stenosis cases, open heart surgery is necessary to replace the stenotic valve with a biological or mechanical valve. In mild cases, however, a dumbbell-shaped balloon (Inoue balloon catheter technique) is used to effectively expand (dehisce) the narrowed commissure. This procedure is called percutaneous transseptal mitral commissurotomy (PTMC). Patients undergoing PTMC can be discharged in 1 to 2 days after the procedure. The procedure can be repeated if one treatment is not sufficiently effective.
Merits of PTMC
- Mitral valve stenosis is a valvular disease with high rate of Afib onset and high risk of cerebral infarction.
- It is necessary to have periodic evaluation of valvular function and intracardiac thrombosis through thoracic/transesophageal echocardiography.
- PTMC is an effective catheter treatment leaving no scars (discharged in 1 to 2 days after procedure).
- If one-time PTMC treatment is not sufficiently effective, the procedure can be repeated multiple times.
Syncope
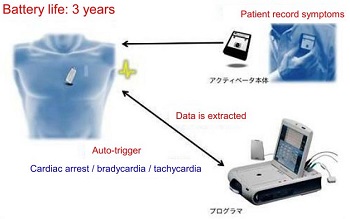
Syncope (blackout) is a temporary loss of consciousness with many different causes. As some syncope cases have been documented to lead to sudden cardiac death, our arrhythmia outpatient clinic sees also patients who have had experienced syncope. Our doctor will speak with you in details about your medical history, order 24-hour ECG (Holter) monitor, and if necessary have you admitted for a detailed examination called electrophysiology study (EPS). Furthermore, to find out the cause of syncope, a loop recorder is implanted below the surface of the skin for 3 years to automatically record any abnormal ECG waves, and to also allow the patient to actively record any symptoms.
Post-CPR
Ventricular fibrillation (Vf) is the most dangerously fatal type of arrhythmia that can lead to death in a short time. In recent years, the remarkable accessibility of AED (automated external defibrillator) has saved many lives. For patients who have been saved by external defibrillator, it is the more important for them to find out the cause of Vf and get treated to prevent sudden death. Patients with Vf coming to our arrhythmia outpatient clinic will receive thorough interview of their medical history, as well as receiving an electrophysiology study (EPS). If necessary, catheter ablation treatment or implantation of ICD or CRTD will also be carried out.
Heart Failure
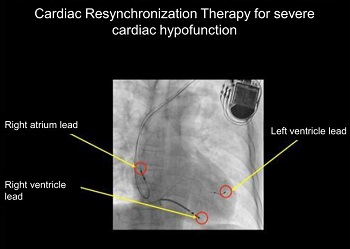
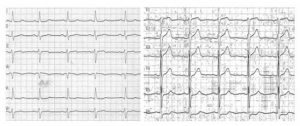
In cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), three leads are placed inside the heart. In the right atrium is a standard pacemaker lead, in the right ventricle is a defibrillation shock lead, and in the left ventricle a special pacemaker lead. The pacemaker device itself is placed below the surface of the skin to your left chest. The pacemaker leads send electrical signals at optimal timing, which help to improve ventricular dyssynchrony. More importantly, in addition to improving heart failure, this treatment gives life-saving shock when fatal arrhythmia occurs.
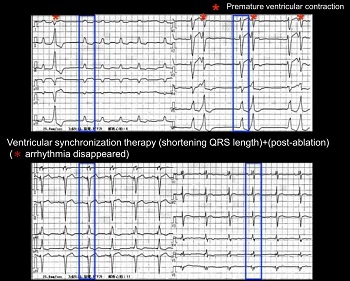
The image to the right show pre- and post-treatment ECGs. The top ECG shows elongated QRS length (blue box) before treatment in comparison to the post-CRT treatment in the bottom ECG, indicating shortened length and improved dyssynchrony. Also, the frequent arrhythmia (*) before treatment was improved with catheter ablation.
Merits of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy for severe cardiac hypofunction
- Effective treatment for improving ventricular dyssynchrony (irregular ventricular contraction).
- Effective treatment for heart failure that does not respond well to drug therapy.
- Effective treatment toward preventing sudden cardiac death from heart failure.
- Effective treatment toward improving prognosis (lifespan) of heart failure patient.
● Device Treatment
Device treatments include pacemaker, ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator), CRT (Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy), and CRTD (Cardiac Resynchronization Defibrillator). After your device implantation, you will return periodically to have your device checked. Our device treatment outpatient clinic is every Monday, Wednesday and Friday mornings. Even if you had your device implanted somewhere else and would like to have it interrogated by us on a regular basis, please do not hesitate to contact us for appointment.
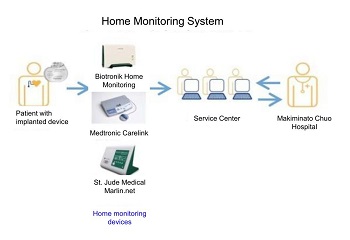
Record on the device can also be accessed remotely.
We are the first on Okinawa to introducing home-monitoring system for ICD patients living in offshore islands. Today, this system is available to everyone with device implantation. Patients receive a home monitoring device which notifies the service center of any arrhythmia events or sends data on a regular basis to the service center. The hospital then have access to these data to respond timely. This home-monitoring system is also usable in nursing homes or other long-term care facilities.
Merits of home-monitoring system
- Useful for discovering events early on and help doctor to determine the necessity of admission.
- Information from the device is effectively managed.
- Cut down travel costs for those who cannot visit the hospital on a regular basis.
Merits and Achievements of Arrhythmia Department
● Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)
APHRS is one of the world renown arrhythmia associations; our Arrhythmia and Heart Failure Department appeared on its January 16, 2016 newsletter.


● Taiwan Heart Rhythm Society AF Ablation 20th Anniversary Forum


● Distinguished Service Awards

● Invited Lectures
- Higa S. (2007) Meet the experts 3: A practical approach to noncontact mapping guided catheter ablation. Final program of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2007)(Taipei, Taiwan, December 18-20, 2007); Page 36.
- Higa S. (2007) Evening symposium (I): Mapping and ablation of atrial fibrillation: bi-atrial mapping. Abstract book of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2007) (Taipei, Taiwan, December 18-20, 2007); Page 32.
- Higa S. (2007) Atrial fibrillation: From bench to the operating theatre: Electrophysiologic mechanisms of thoracic veins for atrial fibrillation initiation and maintenance. Final program of the 10th International Workshop on Cardiac Arrhythmias (Venice Arrhythmias 2007)(Venice, Italy, October 7-10, 2007); Page 52.
- Higa S. (2008) Educational session, Features of new 3D mapping system: A practical approach to noncontact mapping guided catheter ablation for various arrhythmias. Final program of the 4th Complex Catheter Therapeutics (CCT 2008)(Kobe, Japan, January 31-February 2, 2008);Page 43.
- Higa S. (2008) Symposium: Global mapping of chronic AF. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS 2008) in conjunction with 4th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2008)(Raffles, Singapore, November 27-29, 2008);Page 10.
- Higa S. (2009) Expert 1: Complex Arrhythmia Ablation. A practical approach to catheter ablation by 3D mapping for difficult cases. Abstract book of the 2nd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS 2009) in conjunction with 5th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium(APAFS 2009)(Beijing, China, December 22-25, 2009); Final Program Book Page 26.
- Higa S. (2010) Symposium: Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: atrial substrate properties in atrial fibrillation. Abstract book of the 17th World Congress of Cardiology Scientific Sessions (WCC 2010)(Beijing, China, June 16-19, 2010); Page 85.
- Higa S. (2010) Symposium: Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: electrogram-based approach. Abstract book of the 17th World Congress of Cardiology Scientific Sessions (WCC 2010)(Beijing, China, June 16-19, 2010); Page 85.
- Higa S. (2010) Symposium: Circumferential pulmonary vein isolation strategy and additional lines: Evidence-based catheter ablation strategy for atrial fibrillation: trigger, substrate or both? Abstract book of the 17th World Congress of Cardiology Scientific Sessions (WCC 2010)(Beijing, China, June 16-19, 2010); Page 97.
- Higa S. (2010) Electrical and Genetic Analysis for VT: EnSite/NavX System guided catheter ablation of RVOT PVC/VT. Final Program Book Page 73. (3rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 6th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Jeju, Korea, October 28-30, 2010).
- Higa S. (2011) Substrate analysis of ventricular arrhythmias: Non-Contact Mapping Conference- Advanced Class Answering the Non-Contact Mapping Questions in Electrophysiology from Fundamental to Advanced. Endorsed by Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society in Taipei, Taiwan, February 20, 2011).
- Higa S. (2012) Non-contact mapping in atypical AFL: Final Program Book Page 71 (5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6, 2012).
- Higa S. (2013) Non-contact mapping in atypical AFL: Final Program Book Page 114 (6th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session/Cardio Rhythm in conjunction with 9th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Hong Kong, China, October 3-6, 2013).
- Higa S. (2015) Atrial Tachycardia: Current perspective on mechanisms and management. Final Program Book Page(3rd Indonesian Heart Rhythm Society Annual Scientific Meeting in Jakarta, Indonesia, October 23-24, 2015).
- Higa S. (2015) 3D mapping for atrial flutter: Atrial flutter ablation revisited. Final Program Book Page (8th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 11th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Melbourne, Australia, November 19-22, 2015).
- Higa S. (2016) Catecholamine dependent polymorphic VT: Role of Ablation. Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Arrhythmia-4, Specific Type of Inherited VT, Catheter Ablation VII (2nd International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, March 12-13, 2016).
- Higa S. (2016): VT 9: Role of Imaging in VT Ablation: 3D Mapping for idiopathic right vaentricular arrhythmias: RVOT-PVC/VT ablation revisited. Final Program Book Page . (9th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 12th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Seoul, Korea, October 12-15, 2016).
- Higa S. (2017): Idiopathic VPC/VT originating outside the RVOT? when and where do I look outside of the RVOT? (APHRS Ablation Curriculum: Module 3F, Ventricular Tachycardia (VT), Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, July 21-22, 2017).
- Higa S. (2017): Ablation of non-ischemic VT, patient and electrogram characteristics, and outcome. (APHRS Ablation Curriculum: Module 3F, Ventricular Tachycardia (VT), Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, July 21-22, 2017).
- Higa S. (2017): Pros and cons of cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation. Taiwan Heart Rhythm Society AF Ablation 20th Anniversary Forum, Taipei, Taiwan, December 16, 2017).
- Higa S. (2018): Image and anatomy: Multidisciplinary approach for management of cardiac arrhythmias. Role of Imaging in VT: 3D mapping for idiopathic right ventricular arrhythmias. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Ishigaki S. (2018): Case sharing 01: My tough experience of AF ablation: My tough cryoablation case. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A. (2018): Device 03: ICD Trials: Awareness in clinical research and beyond: Inappropriate ICD therapy revisited: How to avoid oversensing of repolarization electrograms. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Higa S. (2019): Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation with the Endoscopic Ablation System: An Overview and Early Experiences. THRS Annual Conference in Conjunction with International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, March 23-, 2019).
- Higa S. (2019): Core Lectures. Computer modeling/ECG/Signal Processing: Role of signal analysis to identify the origin of VT. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Higa S. (2019): Industrial Mini Seminars. Cryoballoon ablation, Improving outcomes in PVI: Think beyond the occlusion: Efficacy and safety of cryoballoon ablation from Japanese experience: How to avoid periprocedural complications. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Maesato A. (2019): Case Based Scenarios. Challenging and interesting CIEDs cases (II/II): Inappropriate ICD therapy revisited: How to avoid oversensing of repolarization electrograms. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
● Invited Moderator at International Conferences
- Higa S. (2012) Meet the experts VT (3) (5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6, 2012).
- Higa S. (2012) Device/Syncope/SCD (5) (5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6, 2012).
- Higa S. (2012) AFL/AT (2) (5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6,2012).
- Higa S. (2015) Moderator: Poster 10 best abstracts on 24th October 2015 (3rd Indonesian Heart Rhythm Society Annual Scientific Meeting in Jakarta, Indonesia, October 23-24, 2015)
- Higa S. (2016) Session Moderator: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Arrhythmia-3, Catheter Ablation VI (2nd International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, March 12-13,2016)
- Higa S. (2017) Session Moderator: Catheter Ablation I-Updated Approach for Brugada Syndrome.(3rd International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, March 10-11,2017).
- Higa S. (2017) Session Moderator: Catheter Ablation IV-Fundamental of VT Ablation for Fellowship Training. (3rd International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, March 10-11, 2017).
- Higa S. (2018): Session Moderator: PSVT 03: Ablation of difficult AVNRT. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Higa S. (2018): Session Moderator : Joint Session 01: Joint session of the International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology. Digital Health: Implications for arrhythmia management. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Higa S. (2018): Session Moderator: Case sharing 01: My tough experience of AF ablation. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Higa S. (2018): Session Moderator: Basic and Translational Medicine 16: Sinus Node Alternans: From Discovery to Patient Care. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Ishigaki S. (2018): Session Moderator: AF 06: Technical consideration for PVI: State of the art, Part II. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A. (2018): Session Moderator: Device 03: ICD Trials: Awareness in clinical research and beyond. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A. (2018): Session Moderator: Device 15: How to manage AF in patients with ICD/CRTD. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
● Chair Person at International Conferences
- Symposium 02: AF02 AF Substrate. Final Program Book Page 33. (3rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 6th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Jeju, Korea, October 28-30, 2010).
- Chaired Poster Session CPS02: Atrial Fibrillation. Final Program Book Page 89. (3rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 6th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Jeju, Korea, October 28-30, 2010).
- Mini-Symposium: AF/AFL/AT: Clinical Studies 1. Final Program Book Page 91. (4rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 7th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Fukuoka, Japan, September 20-22, 2011).
- VT 2: New Treatment for VT/VF. Final Program Book Page . (9th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 12th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Seoul, Korea, October 12-15, 2016).
- How to Session 1: AF/AT 3D Mapping. Final Program Book Page . (9th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 12th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Seoul, Korea, October 12-15, 2016).
● Live Session Panelist at international Catheter Ablation Conferences
- Live Session Panelist (Live case transmission 3). Final program of the 4th Complex Catheter Therapeutics (CCT 2008)(Kobe, Japan, January 31-February 2, 2008); Page 44.
- Live Session Panelist (Live case transmission 2). Final program of the 5th Complex Catheter Therapeutics (CCT 2009)(Kobe, Japan, January 29-31, 2009); Page 44.
- Live Session Panelist (Live case transmission 2). Final program of the 6th Complex Catheter Therapeutics (CCT 2010)(Kobe, Japan, January 28-30, 2010); Page 73.
- Live Session Panelist (Live case 1 Idiopathic). (APHRS Ablation Curriculum: Module 3F, Ventricular Tachycardia (VT), Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan, July 21-22, 2017)
- Live Session Panelist (Live case 2 Substrate). (APHRS Ablation Curriculum: Module 3F, Ventricular Tachycardia (VT), Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan, July 21-22, 2017)
- Live Session Panelist (Live Demo, Ablation). (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Facilitator (VGH Online VT Course 2020, Taipei Veterans General Hospital in Taipei, Taiwan, September 4-6, 2020).
● Live Demonstration of Catheter Ablation at International Conferences
- Higa S, Ishigaki S, Maeda M, Lin YJ, Betty G. (2006) Live demonstration: Catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation. Final program of the 2nd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2006)(Tokyo, Japan, December 23-25, 2006); Page 11.
- Lin YJ, Higa S, Chan CP, Chan YS, Fung WH, Lai WK. (2010) Live demonstration: Non-contact mapping conference. Answering the non-contact mapping questions in electrophysiology. (Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China) August 19-20, 2010.
● Publications (Peer-reviewed Articles)
- Shimabukuro M, Shinzato T, Higa S, Chibana T, Yoshida H, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N. (1995) Enhanced insulin response relates to acetylcholine-induced vasoconstriction in vasospastic angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 25(2):356-361.
- Shimabukuro M, Shinzato T, Higa S, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N. (1995) Impaired mechanical response to calcium of diabetic rat hearts: reversal by nifedipine treatment. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.26(3):495-502.
- Higa S, Shimabukuro M, Shinzato T, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N. (1995) Long-term nifedipine treatment reduces calcium overload in isolated reperfused hearts of diabetic rats (学位取得論文). Gen Pharmacology: The Vascular System.26(8):1679-1686.
- Shimabukuro M, Higa S, Shinzato T, Yoshida H, Nagamine F, Takashiba K, Takasu N. (1996) Successful repair of intimal dissection following coronary angioplasty with a 48-hour inflation of spiral inflation coil and local delivery of heparin. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv.39(1):103-105.
- Shimabukuro M, Higa S, Shinzato T, Nagamine F, Takasu N. (1996) Enhancement of postischemic myocardial stunning by calcium overload in hearts of diabetic rats. Life Sci. 58(15):1291-1299.
- Shinzato T, Shimabukuro M, Higa S, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N. (1996) Effect of gliclazide on the functional response to calcium in diabetic rat heart. Gen Pharmacology: The Vascular System.27(3):471-475.
- Shimabukuro M, Higa S, Shinzato T, Nagamine F, Komiya I, Takasu N. (1996) Cardioprotective effects of troglitazone in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Metabolism. 45(9):1168-1173.
- Yoneda K, Takasu N, Higa S, Oshiro C, Oshiro Y, Shimabukuro M, Asahi T. (1998) Direct effects of thyroid hormones on rat coronary artery: nongenomic effects of triiodothyronine and thyroxine. Thyroid. 8(7):609-613.
- Liu TY, Tai CT, Lee PC, Hsieh MH, Higa S, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2003) Novel concept of atrial tachyarrhythmias originating from the superior vena cava: insight from noncontact mapping. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.14(5):533-539
- Lin CI, Wu SH, Higa S, Chen YC. (2003) Electromechanical abnormality inhereditary cardiomyopathic hamsters and ion channel remodeling. International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism. 5(1):160-163.
- Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Liu TY, Lee PC, Huang JL, Hsieh MH, Yuniadi Y, Huang BH, Lee SH,Ueng KC, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) Focal atrial tachycardia: new insight from noncontact mapping and catheter ablation. Circulation.109(1):84-91.
- Liu TY, Tai CT, Huang BH, Higa S, Lin YJ, Huang JL, Yuniadi Y, Lee PC, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) Functional characterization of the crista terminalis in patients with atrial flutter: Implications for radiofrequency ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 43(9):1639-1645.
- Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Liu TY, Lee PC, Huang JL, Yuniadi Y, Huang BH, Hsieh MH, Lee SH, Kuo JY, Lee KT, Chen SA. (2004) Mechanism of adenosine-induced termination of focal atrial tachycardia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.15(12):1387-1393.
- Wu SH, Chen YC, Higa S, Lin CI. (2004) Oscillatory transient inward currents in ventricular myocytes of healthy versus myopathic Syrian hamster. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 31(10):668-676.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Liu TY, Higa S, Lee PC, Huang JL, Yuniadi Y, Huang BH, Lee KT, Lee SH, UengKC, Hsieh MH, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) Electrophysiological mechanisms and catheter ablation of complex atrial arrhythmias from crista terminalis: Insight from three-dimensional noncontact mapping. PACE.;27(9):1231-1239.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Huang JL, Lee KT, Lee PC, Hsieh MH, Lee SH, Higa S, Yuniadi Y, Liu TY, ChenSA. (2005) Characterization of right atrial substrate in patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.16(2);173-180.
- Yuniadi Y, Tai CT, Lee KT, Huang BH, Lin YJ, Higa S, Liu TY, Huang JL, Lee PC, Chen SA. (2005) A new electrocardiographic algorithm to differentiate upper loop re-entry from reverse typical atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol.46(3):524-528.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Tso HW, Huang JL, Higa S, Yuniadi Y, Huang BH, Liu TY, Lee PC, Hsieh MH, Chen SA. (2005) Electrophysiological characteristics and catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal right atrial fibrillation. Circulation.112(12):1692-1700.
- Tsao HM, Wu MH, Higa S, Lee KT, Tai CT, Hsu NW, Chang CY, Chen SA. (2005) Anatomic relationship of the esophagus and left atrium: Implication for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Chest.128(4):2581-2587.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Tso HW, Higa S, Tsao HM, Chang SL, Hsieh MH, Chen SA. (2006)Frequency analysis in different types of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol.47(7):1401-1407.
- Huang JL, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Huang BH, Lee KT, Higa S, Yuniadi Y, Chen YJ, Chang SL, Lo LW, Wongcharoen W, Ting CT, Chen SA. (2006) Substrate mapping to detect abnormal atrial endocardium with slow conduction in patients with atypical right atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48(3):492-498.
- Lee PC, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Liu TY, Huang BH, Higa S, Yuniadi Y, Lee KT, Hwang B, Chen SA. (2007) Noncontact three-dimensional mapping guides catheter ablation of difficult atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Int J Cardiol.31;118(2):154-163.
- Lin YJ, Higa S, Kao T, Tso HW, Tai CT, Chang SL, Lo LW, Wongcharoen W, Chen SA. (2007) Validation of the frequency spectra obtained from the noncontact unipolar electrograms during atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.18(11):1147-1153.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Chang SL, Wongcharoen W, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Chen YJ, Higa S, Ueng KC, Chen SA. (2008) Consistency of complex fractionated atrial electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm.5 (3):406-412.
- Hsu NW, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Chang SL, Wongcharoen W, Lo LW, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, TsoHW, Chen YJ, Higa S, Chen SA. (2008) Frequency analysis of the fibrillatory activity from surface ECG lead V1 and intracardiac recordings: implications for mapping of AF. Europace.10(4):438-443.
- Udyavar AR, Chang SL, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Tsao HM, Hsieh MH, Hu YF,ChiangSJ, Chen YJ, Wongcharoen W, Higa S, Ueng KC, Chen SA. (2008) The important role of pulmonary vein carina ablation as an adjunct to circumferential pulmonary vein isolation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.19(6):593-598.
- Lin YJ, Kao T, Tai CT, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Tsao HM, Higa S, Chen SA. (2008) Spectral analysis during sinus rhythm predicts an abnormal atrial substrate in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 5(7):968-974.
- Huang JL, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Ueng KC, Huang BH, Lee KT, Higa S, Yuniadi Y, Chang SL, Lo LW, Wanwarang W, Hu YF, Lee PC, Tuan TC, Ting CT, Chen SA. (2008) Right atrial substrate properties associated with age in patients with typical atrial flutter. Heart Rhythm.5(8):1144-1151.
- Chang SH, Chen YC, Chiang SJ, Higa S, Cheng CC, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2008) Increased Ca2+ sparks and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores potentially determine the spontaneous activity of pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. Life Sci. 83(7-8):284-292.
- Lo LW, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Wongcharoen W, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Ueng KC, Tsai WC, Chang CJ, Tsao HM, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) Characteristics of the cavo-tricuspidisthmus in predicting recurrent conduction in the long-term follow-up. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(1):39-43.
- Hu YF, Chen YC, Cheng CC, Higa S, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2009) Fluvastatin reduces pulmonary vein spontaneous activity through nitric oxide pathway. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(2):200-206.
- Lee SH, Chen YC, Cheng CC, Higa S, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2009) Hypertonicity increases rabbit atrium and pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis: A potential contributor to the genesis of atrial fibrillation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36(4):419-424.
- Chang SL, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Chiang SJ, Wongcharoen W,Tsao HM, Ueng KC, Higa S, Lee PC, Chen SA. (2009) Induced atrial tachycardia after circumferential pulmonary vein isolation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: electrophysiological characteristics and impact of catheter ablation on the follow-up results. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(4):388-394.
- Hu YF, Higa S, Huang JL, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Chang CJ, Tsai WC, Lee PC, Ishigaki S, Oyakawa A, Chen SA. (2009) Electrophysiological characteristics and catheter ablation of focal atrial tachycardia with more than one focus. Heart Rhythm. 6(2):198-203.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Chang SL1, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Chang CJ, Tsai WC, Kao T, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) The efficacy of additional ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms for catheter ablation of non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(6):607-615.
- Lo LW, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Ueng KC, Tsai WC, Tuan TC Chang CJ, Kao T, Tsao HM, Wongcharoen W, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) Predicting factors for atrial fibrillation acute termination during catheter ablation procedures: implications for the catheter ablation strategy and long-term outcome. Heart Rhythm. 6(3):311-318.
- Udyavar AR, Huang SH, Chang SL, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Hu YF, Wongcharoen W, Tsao HM, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) Acute effect of circumferential pulmonary vein isolation on left atrial substrate. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(7):715-722.
- Lin YJ, Higa S, Tai CT, Chang SL, Lee KT, Lo LW, Ishigaki S, Tuan TC, Wongcharoen W, Hu YF, Hsieh MH, Tsao HM, Chen SA. (2009) Role of the right atrial substrate in different types of atrial arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm. 6(5):592-598.
- Hu YH, Huang JL, Wu TJ, Higa S, Shih CM, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Chang CJ, Tsai WC, Lee PC, Tsao HM, Ishigaki S, Oyakawa A, Chen SA. (2009) Gender differences of electrophysiological characteristics in focal atrial tachycardia. Am J Cardiol. 104(1):97-100.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Wongcharoen W, Hu YF, Tso HW, Tsai WC, Chang CJ, Ueng KC, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) Spatiotemporal organization of the left atrial substrate after circumferential pulmonary vein isolation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation Arrhythmia & Electrophysiology. 2(3):233-241.
- Chen YC, Pan NH, Cheng CC, Higa S, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2009) Heterogeneous expression of potassium currents and pacemaker currents potentially regulates arrhythmogenesis of pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(9):1039-1045.
- Udyavar AR, Chen YC, Cheng CC, Higa S, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2009) Cariporide (HOE642) attenuates lactic acidosis induced pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis. Life Sci. 85(1-2):19-25.
- Lo LW, Lin YJ, Tsao HM, Chang SL, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Tsai WC, Tuan DC, Chang CJ, Lee PC, Tai CT, Tang WH, Suenari K, Huang SY, Higa S, Chen SA. (2009) Characteristics of complex fractionated electrograms in non-pulmonary vein ectopy initiating atrial fibrillation/atrial tachycardia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(12):1305-1312.
- Lo LW, Lin YJ, Tsao HM, Chang SL, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Ueng KC, Tsai WC, Tuan TC, Chang CJ, Tang WH, Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2009) The impact of left atrial size on long-term outcome of catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 20(11):1211-1216.
- Chang CJ, Lin YJ, Higa S, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Hu YF, Udyavar AR, Tang WH, Tsai WC, Huang SY, Tung NH, Suenari K, Tsao HM, Chen SA. (2010) The disparities in the electrogram voltage measurement during atrial fibrillation and sinus rhythm. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 21(4):393-398.
- Lo LW, Higa S, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Tuan TC, Hu YF, Tsai WC, Tsao HM, Tai CT, Ishigaki S, Oyakawa A, Maeda M, Suenari K, Chen SA. (2010) The novel electrophysiology of complex fractionated atrial electrograms: Insight from noncontact unipolar electrograms. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 21(6):640-648.
- Lo LW, Tsao HM, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Hu YF, Tsai WC, Tuan TC, Suenari K, Huang SY, Tung NH, Higa S, Tai CT, Ueng KC, Li CH, Chao TF, Wu TJ, Chen SA. (2011) Different patterns of atrial remodeling after catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 22(4):385-393.
- Chung FP, Hu YF, Chao TF, Higa S, Cheng Henrich, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Tai CT, Li CH, Lin YK, Chen SA. (2011) The correlation between ventricular repolarization and clinical severity of spinal cord injuries. Heart Rhythm. 8(6):879-874.
- Maesato A, Higa S, Lin YJ, Chinen I, Ishigaki S, Yajima M, Masuzaki H, Chen SA. (2011) Impact of pacing and high-pass filter settings on ventricular bipolar electrograms in implantable cardioverter defibrillator systems: implication of predictors for inappropriate therapy caused by oversensing of repolarization electrograms. Circulation J. 75(9):2095-2104.
- Nakamura K, Takami M, Shimabukuro M, Maesato A, Chinen I, Ishigaki S, Higa S, Keida T, Masuzaki H. (2011) Effective prediction of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy using a novel program of gated myocardial perfusion SPECT. Europace 13(12):1731-1737.
- Chang SL, Chen YC, Hsu CP, Kao YH, Lin YK, MD, Lai YJ, Yeh HI, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2013) Heat shock protein inducer modifies arrhythmogenic substrate and inhibits atrial fibrillation in failing heart. Int J Cardiol. 168(4):4019-4026.
- Chong E, Chang SL, Hsiao YW, Singhal R, Liu SH, Leha T, Lin WY, Hsu CP, Chen YC, Chen YJ, Wu TJ, Higa S, Chen SA. (2015) Resveratrol, a red wine antioxidant, reduces atrial fibrillation susceptibility in the failing heart by PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway activation. Heart Rhythm. 12:1046-1056.(This article was selected one of the most notable 4 basic articles published in 2015 in Heart Rhythm Journal judged by the editors.)
- Dan Do VB, Tsai CW, Lin YJ, Higa S, Yagi N, Chang SL, Lo LW, Chung FP, Liao JN, Chen SA. (2015) The different substrate characteristics of arrhythmogenic triggers in idiopathic right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia: new insight from noncontact mapping. PLoS One. 10(10):e0140167.
- Te AL, Higa S, Chung FP, Lin CY, Lo MT, Liu CA, Lin C, Chang YC, Chang SL, Lo LW, Hu YF, Tuan TC, Chao TF, Liao J1, Chang YT, Lin CH, Hung Y, Yamada S, Pan KL, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2017) The use of a novel signal analysis to identify the origin of idiopathic right ventricular outflow tract ventricular tachycardia during sinus rhythm: simultaneous amplitude frequency electrogram transformation mapping. PLoS One. 12(3):e0173189.
- Oginosawa Y, Kohno R, Honda T, Kikuchi K, Nozoe M, Uchida, T, Minamiguchi H, Sonoda K, Ogawa M, Ideguchi T, Kisaki Y, Nakamura T, Oba K, Higa S, Yoshida K, Tsunoda S, Fujino Y, Abe H. (2017) Superior rhythm discrimination by the SST algorithm: results of the Defibrillator shock reduction with Enhanced features and Settings of implantable cardiac device (DEFENSE) Trial. Circulation J. 81(9);1272-1277.
- Yamada S, Lin CY, Chang SL, Chao TF, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chung FP, Hu YF, Tuan TC, Liao JN, Te AL, Chang YT, Chang TY, Wu CI, Higa S, Chen SA. (2017) Risk of stroke in patients with short-run atrial tachyarrhythmia. Stroke 48(12):3232-3238.
- Yamada S, Fong MC, Hsiao YW, Chang SL, Tsai YN, Lo LW, Chao TF, Lin YJ, Hu YF, Chung FP, Liao JN, Chang YT, Li HY, Higa S, Chen SA. (2018) Impact of Renal denervation on atrial arrhythmogenic substrate in ischemic models of heart failure. JAHA 7(2): e007312.
- Chang CJ, Cheng CC, Chen YC, Higa S, Huang JH, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2018) Factor Xa inhibitors differently modulate electrical activities in pulmonary veins and the sinoatrial node. European J Pharmacology. 833:462-471.
- Chang SL, Hsiao YW, Tsai YN, Lin SF, Liu SH, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chung FP, Chao TF, Hu YF, Tuan TC, Liao JN, Hsieh YC, Wu TJ, Higa S, Chen SA. (2018) Interleukin-17 enhances cardiac ventricular remodeling via activating MAPK pathway in ischemic heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. pii: S0022-2828(18)30767-3. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.005. PMID: 30096409
- Wu CI, Lu YY, Chen YC, Lin FZ, Huang JH, Lin YK, Higa S, Chan CS, Liu CM, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2020) The AMP-activated protein kinase modulates hypothermia-induced J wave. Eur J Clin Invest. 50(6) e13247. doi: 10.1111/eci.13247.PMID: 32307703
- Chang TY, Hsiao YW, Guo SM, Chang SL, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Hu YF, Chung FP, Chao TF, Liao JN, Tuan TC, Lin CY, Higa S, Chen SA. (2020) Resistin as a biomarker for the prediction of left atrial substrate and recurrence in patients with drug-refractory atrial fibrillation undergoing catheter ablation. Int Heart J. 61 (3): 517-523. doi: 10.1536/ihj.19-680. PMID: 32418972
- Liu CM, Lin FJ, Chen YC, Lin YK, Lu YY, Wu CI, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2020) Concurrent increases in post-pacing action potential duration and contractility predict occurrence of ventricular arrhythmia. Pflugers Arch. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02445-7. PMID: 32794054
- Hsiao YW, Tsai YN, Huang YT, Liu SH, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Hu YF, Chung FP, Lin FS, Chang SL, Higa S, Chen SA. (2020) Rhodiola crenulata reduces ventricular arrhythmia through mitigating the activation of IL-17 and inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07072-z. PMID: 32946036
- Lkhagva B, Lin YK, Chen YC, Cheng WL, Higa S, Kao YH, Chen YJ. (2021) ZFHX3 knockdown dysregulates mitochondrial adaptations to tachypacing in atrial myocytes through enhanced oxidative stress and calcium overload. Acta Physiol (Oxf).e13604. doi: 10.1111/apha.13604. PMID: 33332716
- Tsai YN, Hsiao YW, Lin SF, Chan YH, Hsieh YC, Tang WH, Lee AS, Huang YT, Li HY, Chao TF, Higa S, Wu TJ, Chang SL, Chen SA. (2021) Proinflammatory cytokine modulates intracellular calcium handling and enhances ventricular arrhythmia susceptibility. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.623510. eCollection 2021.PMID: 33796569
- Tsai YN, Cheng WH, Chang YT, Hsiao YW, Chang TY, Hsieh YC, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chao TF, Kuo MJ, Higa S, Chang SL, Chen SA. (2021) Mechanism of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor in suppression of ventricular arrhythmia. J Cardiol. S0914-5087(21)00108-8. doi:10.1016/j.jjcc.2021.04.011. PMID: 34059408
- Chang TY, Lo LW, Te ALD, Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Hu YF, Chung FP, Lin CY, Chao TF, Liao JN, Tuan TC, Kuo L, Wu CI, Liu CM, Jain A, Lugtu IC, Higa S, Chen SA. (2021) Deep sedation with intravenous anesthesia is associated with outcome in patients undergoing cryoablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Int Heart J. doi: 10.1536/ihj.20-819. PMID: 34234078
- Tsukahara K, Oginosawa Y, Fujino Y, Honda T, Kikuchi K, Nozoe M, Uchida T, Minamiguchi H, Sonoda K, Ogawa M, Ideguchi T, Kizaki Y, Nakamura T, Oba K, Higa S, Yoshida K, Yagyu K, Miyamoto T, Yasunobu Y, Ohe H, Kohno R, Kataoka M, Otsuji Y, Abe H. (2021) RR interval variability in the evaluation of ventricular tachycardia and effects of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy. J Arrhythmia. (in press).
- Liu CM, Liu CL, Hu KW, Tseng VS, Chang SL, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chung FP, Chao TF, Tuan TC, Liao JN, Lin CY, Chang TY, Fann CSJ, Higa S, Yagi N, Hu YF, Chen SA. (2022) A deep learning-enabled electrocardiogram model for the identification of a rare inherited arrhythmia: Brugada syndrome. Can J Cardiol. 38(2):152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.08.014. PMID: 34461230
- Chang JH, Cheng CC, Lu YY, Chung CC, Yeh YH, Chen YC, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2021) Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1/NOS pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 911:174547. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174547.
- Huang SY, Chen YC, Kao YH, Lu YY, Lin YK, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2021) Calcium dysregulation increases right ventricular outflow tract arrhythmogenesis in rabbit model of chronic kidney disease. J Cell Mol Med. Dec;25(24):11264-11277. Epub 2021 Nov 10. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17052. PMID: 34761510
- Cheng WL, Chen YC, Li SJ, Lee TI, Lee TW, Higa S, Chung CC, Kao YH, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2022) Galectin-3 enhances atrial remodelling and arrhythmogenesis through CD98 signalling. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 234(3):e13784. doi: 10.1111/apha.13784. PMID: 34995420
- Lu YY, Cheng CC, Huang SY, Chen YC, Kao YH, Lin YK, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2022) Fibroblast growth factor 1 reduces pulmonary vein and atrium arrhythmogenesis via modification of oxidative stress and sodium/calcium homeostasis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 8:813589. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.813589. eCollection 2021.PMID: 35118146
- Liu CM, Edward S.C. Shih, Chen JY, BS, Huang CH, Wu IC, Chen PF, Higa S, Yagi N, Hu YF, Hwang MJ, Chen SA. (2022) Artificial intelligence-enabled electrocardiogram improves the diagnosis and prediction of mortality in patients with pulmonary hypertension. JACC: Asia; 2(3):258-270. doi:10.1016/j.jacasi.2022.02.008. PMID: 36338407
- Liu CM, Hsieh ME, Hu YF, Wei TY, Wu IC, Chen PF, Lin YJ, Higa S, Yagi N, Tseng VS, Chen SA, (2022) Artificial intelligence-enabled model for early detection of left ventricular hypertrophy and mortality prediction in young to middle-aged adults. Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. 15(8): e008360. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.121.008360. PMID: 35959675
- Lu YY, Lin FJ, Chen YC, Kao YH, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2022) Role of endothelin-1 in right atrial arrhythmogenesis in rabbits with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. 23(19):10993. doi: 10.3390/ijms231910993.PMID: 36232308
- Liu CH, Chen YC, Lu YY, Lin YK, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2022) Gender difference in lithium-induced sodium current dysregulation and ventricular arrhythmogenesis in right ventricular outflow tract cardiomyocytes. Biomedicines. 10(11):2727. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10112727. PMID: 3635925.
- Chan CS, Lin FJ, Liu CM, Lin YK, Chen YC, Hsu CC, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2022) Mirabegron, a β3‑adrenoreceptor agonist, regulates right and left atrial arrhythmogenesis differently. Exp Ther Med. 18;24(6):720. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11656. PMID: 36340605
- Chin CG, Ahmed ME, Lin FJ, Chen YC, Lin YK, Lu YY, Higa S, Chen SA, Hsieh MH, Chen YJ. (2022) Effects of adrenomedullin on atrial electrophysiology and pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 23(22):14064. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214064.PMID: 36430541
● Review Articles and Editorials
Review Articles
- Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2006)Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation originating from extra pulmonary vein areas: Taipei approach. Heart Rhythm. ;3:1386-1390.
- Higa S, Chen SA. (2006) Focal atrial tachycardia. J Arrhythmia .22(3):132-148.
- Higa S, Lo LW, Chen SA. (2018) Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation originating from non-pulmonary vein areas. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol Rev. 7(4):273-81. DOI:https://doi.org/10.15420/aer.2018.50.3
- Suenari K, Nakano T, Tomomori S, Shiode N, Higa S, Chen SA. (2020) Cryoballoon ablation for patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation Reports. 2(2):75-82.
- Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Suenari K, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2021) Diabetes and endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism) as risk factors for atrial fibrillation. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 13(1):63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2020.11.005.
- Lkhagva B, Lee TW, Lin YK, Chen YC, Chung CC, Higa S, Chen YJ. Disturbed cardiac metabolism triggers atrial arrhythmogenesis in diabetes mellitus: energy substrate alternate as a potential therapeutic intervention. Cells. 11(18):2915. doi: 10.3390/cells11182915.
Editorials
- Chen SA, Higa S. Editorial: The roles of anatomy, image, and electrogram voltage in ablation of cavotricuspid isthmus. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2005;12:13-15.
- Boukens BJ, Baartscheera A, Higa S. Editorial Comment: Arrhythmogenic pulmonary vein myocardium in heart failure. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38(10):654-655.
- Higa S. (2020) Editorial to “Diverse activation patterns during persistent atrial fibrillation by non-contact charge-density mapping of human atrium”. J Arrhythmia. 36(4):703-704. doi: 10.1002/joa3.12373. eCollection. PMID: 32782642
● Book Chapters
Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2006) Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation originating from the non-pulmonary vein areas. In: Huang S and Wood M, editors. 1st edition of Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, USA; Page 289-304
Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2008) Focal atrial tachycardias. In: Wilber DJ, Packer DL, Stevenson WG, editors. 3rd edition of Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias: Basic concepts and clinical applications. Blackwell Futura, Malden, MA, USA; Page 105-119.
Higa S, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2008) Noncontact mapping. In: Calkins H, Jais P, Steinberg J, editors. 1st edition of A practical approach to catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, USA; Page 118-133.
Higa S, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chang SL, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2011) Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation originating from the non-pulmonary vein areas. In: Huang S and Wood M, editors. 2nd edition of Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, USA; Page 265-279.
Higa S, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chang SL, Hu YF, Chen SA. (2014) Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation originating from the non-pulmonary vein areas. In: Huang S and Wood M, editors. 3rd edition of Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, USA ;page 288-304.

Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Suenari K, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2021) Diabetes and endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism) as risk factors for atrial fibrillation. In: Shenasa S, Sanders P, Nattel S, editors. Risk factors in atrial fibrillation: appraisal of AF risk stratification. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, USA; Page 63-75. In: Thakur RK and Natale A, consulting editors. 13(1) Cardiac Electrophysiology Clinics: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1877-9182(21)00003-4
● Presentations at International Conferences
- Shinzato T, Higa S, Shimabukuro M, Chibana T, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Mimura G. (1993) Effects of calcium concentration on cardiac function in diabetic rats. Abstract book of the 7th Korea-Japan Symposium on Diabetes Mellitus (Seoul, Korea, April 13-14, 1993); Page 70.
- Shimabukuro M, Shinzato T, Higa S, Nakada Y, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Mimura G. (1993) Improvement of basal and post-ischemic myocardial function by gliclazide on isolated perfused hearts from diabetic rats: effects of calcium overload. Abstract book of the 7th Korea-Japan Symposium on Diabetes Mellitus (Seoul, Korea, April 13-14, 1993); Page 71.
- Shimabukuro M, Higa S, Shinzato T, Chibana T, Yoshida H, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N,Mimura G. (1993) Enhanced insulin secretion relates to coronary vasoconstriction in humans. Abstract book of the 4th Japan-China Symposium on Diabetes Mellitus (Yokohama, Japan, October 7-8, 1993); Page 58.
- Higa S, Shimabukuro M, Shinzato T, Nagamine F, Murakami K, Takasu N. (1994) Nifedipine treatment improves ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rat hearts. Final program of the 15th International Diabetes Federation Congress (Kobe, Japan, November 6-11, 1994); Page181.
- Higa S, Yoshida H, Oshiro C, Yagi N, Shimabukuro M, Chibana T, Takasu N, Chen SA. (2001) A new electroanatomic guidance for circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary veinostia in patients with focal sources of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 104 (Suppl. II): Page 408. (Annual Scientific Sessions of American Heart Association in Anaheim, CA, USA, November 11-14,2001).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Liu TY, Chen SA. (2003) Non-contact mapping identifies the termination mechanisms and guides ablation of complex atrial flutter. PACE. Vol.26 (Suppl. II): PageS28. (XIIth World Congress on Cardiac Pacing and Electrophysiology in Hong Kong, China, February19-22, 2003).
- Liu TY, Tai CT, Higa S, Chen SA. (2003) Anisotropic conduction velocity in crista terminalis during atypical atrial flutter. PACE. Vol.26 (Suppl. II): Page S49. (XIIth World Congress on Cardiac Pacing and Electrophysiology in Hong Kong, China, February 19-22, 2003).
- Liu TY, Tai CT, Lee PC, Higa S, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2003) Relation between conduction gap and anisotropic property of the crista terminalis in patients with atrial arrhythmias. PACE. Vol.26 (Suppl. II): Page 1052. (24th Annual Scientific Sessions of North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology in Washington, DC, USA, May 14-17, 2003).
- Liu TY, Tai CT, Lee PC, Higa S, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2003) Ablation strategy is different for crista terminalis gaps and conduction channels in complex atrial arrhythmia. PACE. Vol.26 (Suppl. II):Page 1052. (24th Annual Scientific Sessions of North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology in Washington, DC, USA, May 14-17, 2003).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Liu TY, Huang JL, Lee PC, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2003) Fast Fourier transform analysis of noncontact atrial electrograms in atrial flutter and fibrillation. PACE. Vol.26(Suppl. II):Page 1093. (24th Annual Scientific Sessions of North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology in Washington, DC, USA, May 14-17, 2003).
- Huang JL, Tai CT, Higa S, Chen SA. (2003) Changes of dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation during atrial dilation: implication for stretch mechanism from biatrial non-contact mapping. PACE.Vol.26 (Suppl II): Page 1107. (24th Annual Scientific Sessions of North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology in Washington, DC, USA, May 14-17, 2003).
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Liu TY, Higa S, Huang BH, Yuniadi Y, Lai TH, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2003) Validation of atrial activation from the noncontact and contact electrogram using noncontact mapping. Circulation. 108 (Suppl. IV): Page 323. (Annual Scientific Sessions of American Heart Association in Orland, CA, USA, November 9-12, 2003).
- Yuniadi Y, Tai CT, Huang BH, Higa S, Liu TY, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2003) Non-contact mapping of right atrium during typical atrial flutter with variable ECG morphologies. Circulation. 108 (Suppl. IV): Page 542. (Annual Scientific Sessions of American Heart Association in Orland, CA, USA, November 9-12, 2003).
- Yuniadi Y, Tai CT, Lee KT, Huang BH, Lin YJ, Higa S, Liu TY, Huang JL, Lee PC, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) A new ECG algorithm to differentiate upper loop reentry from clockwise typical atrial flutter. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1(1)(Suppl.): Page S2-3. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Huang JL, Tai CT, MD, Liu TY, Lee PC, Higa S, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) The Eustachian ridge is not always a barrier of the reentry circuit during typical atrial flutter: a novel finding. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1(1)(Suppl.): Page S19-20. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Lee PC, Tai CT, Liu TY, Higa S, Ding YA, Huang B, Chen SA. (2004) Nominal concept of dual atrioventricular nodal physiology: insight from noncontact mapping. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1 (1)(Suppl.): Page S46. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Liu TY, Lee PC, Huang JL, Ding YA, Chen SA. (2004) Spontaneous termination of human atrial flutter: a novel observation and implication for catheter ablation. HeartRhythm.Vol.1 (1)(Suppl.): Page S55. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2004) Focal atrial tachycardia dose not show radial activation pattern: implication for catheter ablation. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1 (1)(Suppl.): Page S56.(25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22,2004).
- Huang BH, Tai CT, Tsao HM, Higa S, Lee KT, Lin YJ, Yuniadi Y, Chen SA. (2004) High resolution non-contact mapping of right atrial activation during sinus rhythm in humans. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1(1)(Suppl.): Page S167. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Yuniadi Y, Lin YJ, Lee KT, Huang BH, Chen SA. (2004) Novel mechanism of adenosine induced termination of focal atrial tachycardia. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1 (1)(Suppl.):PageS199. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May19-22, 2004).
- Chen SA, Tai CT, MD, Liu TY, Higa S, Lee PC, Ding YA. (2004) Catheter ablation of right atrial substrate in a specific group of patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. Vol.1 (1)(Suppl.): Page S172. (25th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 19-22, 2004).
- Higa S, Chen YC, Wei J, Shimabukuro M, Lin CI. (2004) Electrophysiological effects of palmitate on rabbit pulmonary vein myocardial cells. Abstract book of the 31st International Congress on Electrocardiology (Kyoto, Japan, June 27-July 1, 2004); Page 152.
- Lee PC, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Liu TY, Higa S, Huang B, Chen SA. (2005) The different characteristics of atrial electrograms inside and outside Koch’s triangle. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 2 (5)(Suppl.): PageS189. (26th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in New Orleans, LA,USA, May 4-7, 2005).
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Higa S, Chen SA. (2005) Electrophysiologic characteristics and catheter ablation in patients with Lewis right atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 2 (5)(Suppl.): Page S195. (26th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in New Orleans, LA, USA, May 4-7,2005).
- Tsao HM, Wu MH, Higa S, Lee KT, Tai CT, Huang BH, Hsieh MH, MD, Kuo JY, Chen SA. (2005) Catheter ablation within the coronary sinus carries a risk of esophageal injury. Heart Rhythm. Vol.2 (5)(Suppl.): Page S240. (26th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in New Orleans, LA, USA, May 4-7, 2005).
- Tsao HM, Wu MH, Higa S, Lee KT, Tai CT, Huang BH, Hsieh MH, Kuo JY, Chen YJ, Chen SA.(2005) The important role of detecting pulmonary vein stenosis before catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 2 (5)(Suppl.): Page S276. (26th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in New Orleans, LA, USA, May 4-7, 2005).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2005) A novel finding of sinus node shifting after overdrive pacing and isoproterenol. Circulation. Vol. 112 (17)(Suppl. II): Page 698. (Annual Scientific Sessions of American Heart Association in Dallas, TX, USA. November 13-16, 2005).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2005) Topography of electrical connection between the right atrium and superior vena cava: implication for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation originating from superior vena cava. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2005)(Seoul, Korea, December 15-17, 2005); Page 161.
- Higa S, Tai CT, Chen SA. (2005) Novel characteristics of the electrical breakthroughs from the right atrium to superior vena cava: implication for catheter ablation. Abstract book of the 1stAsia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2005)(Seoul, Korea, December 15-17, 2005);Page178.
- Lin YJ, Tai CT, Higa S, Chen SA. (2005) Different characteristics of right atrial substrate in patients with typical and atypical right atrial flutters. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2005)(Seoul, Korea, December 15-17, 2005); Page 181.
- Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2006) A novel technique of high-density mapping of QS area for catheter ablation of focal atrial tachycardia. Heart Rhythm. 2006;Vol. 3 (5)(Suppl.): PageS244-245. (27th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, May 17-20,2006).
- Lin YJ, Higa S, Tai CT, Wongcharoen W, Chang SL, Lo LW, Chen SA. (2007) Validation of the frequency spectra obtained from the noncontact unipolar electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 4 (5)(Suppl.): Page S185. (28th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Denver, CO, USA, May 9-12, 2007).
- Higa S, Lin YJ, Tai CT, Ishigaki S, WangCharoen W, Chang SL, Lo LW, Chen SA. (2007) Acute atrial pressure overload modulates dominant frequency in patients with atrial fibrillation: new insight from biatrial noncontact mapping in human. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 4 (5)(Suppl.): PageS317.(28th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Denver, CO, USA, May 9-12,2007).
- Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2007) High density mapping of QS area to detect sinus node impulse shifting after beta-adrenergic stimulation. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 4 (5)(Suppl.): Page S350.(28th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Denver, CO, USA, May 9-12,2007).
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Tsao HM, Maeda M, Oyakawa A, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2007) Left atrial roof aneurysm with coronary artery fistula in patient with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a case report. Abstract book of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2007)(Taipei, Taiwan, December 18-20, 2007); Page 174.
- Lo LW, Tai CT, Higa S, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Wongcharoen W, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Chen SA.(2007) Prospective implication of waveform analysis from high-density mapping in patients with atrial fibrillation. Abstract book of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS2007)(Taipei, Taiwan, December 18-20, 2007); Page 207.
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Maeda M, Oyakawa A, Chen SA. (2007) Discordance of conduction block lines in the left atrium in patients with atrial fibrillation: new insight into catheter ablation. Abstract book of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS2007)(Taipei, Taiwan, December 18-20, 2007); Page 246.
- Higa S, Ishigaki S, Tsao HM, Maeda M, Oyakawa A, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2008) Left atrial roof aneurysm with coronary artery fistula in a patient with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a novel case report. Heart Rhythm. 2008;Vol. 5 (5)(Suppl.): Page S204-205. (29th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 14-17, 2008).
- Lin YJ, Higa S, Tai CT, Chang SL, Lo LW, Chen SA. Mechanism responsible for the maintenance of atrial fibrillation: insight from simultaneous bi-atrial activation and frequency mapping. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS2008) in conjunction with 4th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS2008)(Raffles, Singapore, November 27-29, 2008); Page 251.
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Tsao HM, Oyakawa A, Chinen I, Maesato A, Iha K, Shimajiri M, Lin YJ, ChenSA. (2008) Repetitive pleomorphic ventricular tachycardia triggered by ventricular premature contraction originating from idiopathic left ventricular aneurysm in a patient resuscitated from ventricular fibrillation: a novel case report. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS 2008) in conjunction with 4th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2008)(Raffles, Singapore, November 27-29, 2008);Page 339.
- Lo LW, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Udyavar AR, Hu YF, Ueng KC, Tsai WC, Tuan TC, Chang CJ, Tsao HM, Wongcharoen W, Lee PC, Higa S, Chen SA. (2008) Spatiotemporal characterization of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in non-pulmonary vein ectopy initiating atrial fibrillation/atrial tachycardia. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS 2008) in conjunction with 4th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS2008)(Raffles, Singapore, November 27-29, 2008); Page 364.
- Oyakawa A, Higa S, Ishigaki S, Chinen I, Maesato A, Iha K, Shimajiri M, Lin YJ, Chen SA. (2008)Successful ablation of focal atrial tachycardia originating from the right pulmonary vein carina after the Cox-Maze IV procedure in a patient with atrial septal defect under guidance of CARTOMerge technique: A novel case report. Abstract book of the 1st Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session (APHRS 2008) in conjunction with 4th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (APAFS 2008)(Raffles, Singapore, November 27-29, 2008); Page 368.
- Higa S, Lin YJ, Ishigaki S, Chen YJ, Chen SA. (2010) Adenosine-triphosphate modulates dominant frequency in patients with atrial fibrillation: New insight from biatria lnoncontact mapping in human. Heart Rhythm. 2010;Vol. 5 (5)(Suppl.): Page S200. (31th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Denver, CO, USA, May 12-15, 2010).
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Maesato A, Chinen I, Lin YJ, Masuzaki H, Chen SA. (2010) Successful ablation of six tachyarrhythmias during a single ablation procedure. J Arrhythmia. 2010;Vol. 26 (10)(Suppl.):Page 189. (3rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 6th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Jeju, Korea, October 28-30, 2010).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Chinen I, Ishigaki S, Lin YJ, Masuzaki H, Chen SA. (2010) VF induction during automatic measurement of lead impedance by dual chamber implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in a patient with LQT3 plus Brugada syndrome. J Arrhythmia. 2010;Vol. 26 (10)(Suppl.): Page 31.(3rd Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 6th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Jeju, Korea, October 28-30, 2010).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Chinen I, Ishigaki S, Lin YJ, Yajima M, Tatsu K, Obunai K, Uechi Y, Sugama M, Masuzaki H, Chen SA. (2011) Effects of pacing and high-pass filter settings on ventricular bipola relectrograms in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator systems: implication for inappropriate shocks due to T wave oversensing. J Arrhythmia. 2011;Vol. 27 (9)(Suppl.): Page 377. (26th Japanese and 4th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 7thAsia-PacificAtrial Fibrillation Symposium in Fukuoka, Japan, September 20-22, 2011).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Chinen I, Ishigaki S, Lin YJ, Yajima M, Tatsu K, Obunai K, Uechi Y, Sugama M, Masuzaki H, Chen SA. (2011) Predictor for inappropriate shocks due to T wave oversensing using the R and T wave amplitudes of ventricular bipolar electrograms in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator systems. J Arrhythmia. 2011;Vol. 27 (9)(Suppl.): Page 377. (26th Japanese and 4th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 7th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Fukuoka, Japan, September 20-22, 2011)
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Maesato A, Lin YJ, Tatsu K, Obunai K, Uechi Y, Sugama M, Chen SA. (2011) Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome in a patient with hyperthyroidism. J Arrhythmia. 2011;Vol. 27 (9)(Suppl.): Page 453. (26th Japanese and 4th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 7th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Fukuoka, Japan, September 20-22, 2011).
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Maesato A, Lin YJ, Tatsu K, Obunai K, Uechi Y, Sugama M, Yagi N, Chen SA. (2011) Reversal of tachycardiomyopathy in a patient with incessant form ventricular tachycardia originating from left sinus of Valsalva after successful ablation guided by EnSite NavXsystem. J Arrhythmia. 2011;Vol. 27 (9)(Suppl.): Page 458. (26th Japanese and 4th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 7th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Fukuoka, Japan, September 20-22, 2011).
- Ishigaki S, Higa S, Maesato A, Tatsu K, Nomura T, Maehira M, Uezu T, Uechi Y, Sugama M.(2012) Successful CFAE Ablation in a Patient with Permanent Atrial Fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2012;Vol.28 (10)(Suppl.): Page. 195.(5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6, 2012).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Ishigaki S, Tatsu K, Nomura T, Maehira M, Uezu T, Uechi Y, Sugama M. (2012) Persistent tachycardia originating from superior vena cava in a patient with previous history of hyperthyroidism. J Arrhythmia. 2012;Vol. 28 (10)(Suppl.): Page 195. (5th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 8th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Taipei, Taiwan, October 3-6, 2012).
- Chung FP, Lin YJ, Lo LW, Chang SL, MD, Hu YF, Chao TF, Higa S, Chen SA. (2013) Long-term recurrence of right ventricular outflow tract ventricular arrhythmias after catheter ablation: prognostic value of Holter examination during longitudinal follow-up. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 10 (5)(Suppl.): Page S284. (34th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Denver, CO,USA, May 8-11, 2013).
- Higa S, Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Tatsu K, Nomura T, Maehira M, Uezu T, Uechi Y, Sugama M. (2013) Successful isolation of arrhythmogenic area in a patient with focal atria ltachycardia originating from para-Hisian region. J Arrhythmia. 2013;Vol. 29 (10)(Suppl.): Page 170.(6th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session/Cardio Rhythm in conjunction with 9th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Hong Kong, China, October 3-6, 2013.
- Higa S, Lin YJ, MD, Lo MT, Chen Lin C, Chang YC, Lo LW, Chung FP, Liao J, Chiou CW, Chen SA. (2015) The Use of a novel signal analysis to quantify the substrate and identify the origin for idiopathic right ventricular outflow tract ventricular tachycardia during sinus rhythm. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 12 (5)(Suppl.): Page S286. (36th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, May 13-16, 2015).
- Tatsu K, Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Sugama M, Uezu T. (2015) Successful treatment of subacute amiodarone-induced lung toxicity in a patient with perioperative ventricular tachycardia after an aortic valve replacement. J Arrhythmia. 2015;Vol. 31 (10)(Suppl.): Page.(8th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 11th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Melbourne, Australia, November 19-22, 2015).
- Yagi N, Higa S. (2015) Successful treatment of selenium deficiency-induced dilated cardiomyopathy in a patient with Crohn’s disease. J Arrhythmia. 2015;Vol. 31 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (8th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 11th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Melbourne, Australia, November 19-22, 2015).
- Abe H, Kohno R, Honda T, Kikuchi K, Nozoe M, Uchida, T, Minamiguchi H, Sonoda K, Ogawa M, Ideguchi T, Kisaki Y, Nakamura T, Oba K, Higa S, Yoshida K, Tsunoda S,Oginosawa Y. (2016) Reduction of inappropriate therapy by a new algorithm: results from DEFENSE Trial (Defibrillator shock reduction with Enhanced features and Settings of implantable cardiac device) Heart Rhythm. Vol. 13 (5)(Suppl.): Page S – . (37th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 4-7, 2016).
- Yagi N, Higa S. (2016) Significant impact of obstructive sleep apnea in a patient with an incessant form of ventricular tachycardia originating from the left sinus of Valsalva. J Arrhythmia. 2016;Vol. 32 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (9th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 12th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Seoul, Korea, October 12-15, 2016).
- Higa S, Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N. (2016) Early detection of active bleeding from the superficial branch of the femoral artery after cryoballoon ablation in a patient with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2016;Vol. 32 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (9th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 12th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Seoul, Korea, October 12-15, 2016).
- Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N. (2017) Successful cryoballoon ablation in a patient with recurrent long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation after surgical left atrial Maze and mitral valve replacement. J Arrhythmia. 2017;Vol. 33 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (10th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session, 13th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in conjunction with the 64th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society in Yokohama, Japan, September 14-17, 2017).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Ishigaki S, Yagi N. (2017) Successful cryo-ablation in a patient with recurrent focal atrial tachycardia originating from para-Hisian region. J Arrhythmia. 2017;Vol. 33(10)(Suppl.): Page. (10th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session, 13th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in conjunction with the 64th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society in Yokohama, Japan, September 14-17, 2017).
- Maesato A, Higa S, Ishigaki S, Yagi N. (2017) Significant impact of cardiac resynchronization therapy on recurrent long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation in a patient with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Arrhythmia. 2017; Vol. 33 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (10th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session, 13th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in conjunction with the 64th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society in Yokohama, Japan, September 14-17, 2017).
- Chang TY, Lo LW, Higa S, Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Chung FP, Chao TF, Liao JN, Hu YF, Lin CY, Tuan TC, Chang YT, Chen SA. Deep sedation with intravenous anesthesia is associated with a better outcome in patients undergoing cryoablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, Vol. 15 (5)(Suppl.) Page S333. (39th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, May 9-12, 2018).
- Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful cryo-ablation in a patient with frequent ventricular premature contractions originating from the para-Hisian region. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018)
- Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful cryo-ablation in a patient with repeated recurrences of a para-Hisian Kent bundle after multiple radiofrequency ablation procedures. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018)
- Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful ablation of a unique recurrent atrial tachycardia after cryoballoon based box isolation in a patient with long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018)
- Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful cryoballoon based box isolation in a patient with recurrent long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation after a surgical left atrial MAZE and cryoballoon based pulmonary vein isolation. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018)
- Ishigaki S, Maesato A, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) A false positive FDG PET scan due to inflammation after a cryoballoon based pulmonary vein isolation mimicking a metastatic lymph node in a patient with early stage lung cancer. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful cryoballoon based ablation of recurrent persistent ridge-related atrial tachycardia in a patient with long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful cryoballoon based box isolation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation in a patient with an inferior common trunk. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful ablation of ventricular tachycardia storm in a patient with end-stage cardiac sarcoidosis. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018) Successful ablation of ventricular tachycardia storm in a patient with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Yagi N, Higa S. (2018). Transient mild hyperkalemia induced T-wave oversensing causing an intermittent loss of biventricular pacing in a patient with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Arrhythmia. 2018; Vol. 34 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (11th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 14th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium and 4th International Forum of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Taipei, Taiwan, October 17-20, 2018).
- Wu CI, Lu YY, Chen YC, Lin FZ, Huang JH, Lin YK, Higa S, Chan CS, Chen SA, Chen YJ. AMP inhibition suppresses hypothermia-induced J wave and ventricular arrhythmogenesis. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 16 (5)(Suppl.): Page S154. (40th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in San Francisco, CA, USA, May 8-11, 2019).
- Kaneko S, Takemoto M, Asano T, Sakagami S, Takei A, Suzuki M, Mine T, Hayashi K, Kishihara J, Fukaya H, Miura F, Higa S, Kumagai K, Kurata M, Tao C, Warita S. (2019). Faster mapping for targeted atrial fibrillation ablation using a novel algorithm with a high-density grid style catheter in a Japanese population. J Arrhythmia. 2019; Vol. 35 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Takemoto M, Warita S, Mine T, Sakagami S, Asano T, Takei A, Suzuki M, Higa S, Miura F, Okano Y, Tao C, Kaneko S. (2019). Impact of high-density grid style catheter wave mapping on ablation strategy in de novo and redo paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2019; Vol. 35 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Liu CM, Lin FJ, Chen YC, Lin YK, Lu YY, Wu CI, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2019) Concordant increase of post-pacing action potential duration and contractility predicts occurrence of ventricular arrhythmia in Brugada syndrome model. J Arrhythmia. 2019; Vol. 35(10)(Suppl.): Page. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Kuo MJ, Lin YJ, Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Lo MT, Chiang CH, Chang SL, Lo LW, Hu YF, Chung FP, Lin CY, Chang TY, Liu SH, Cheng WH, Liu CM, Kuo L, Chen SA. Electrophysiologically guided pulmonary vein isolation and substrate in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation using PRISM index: a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 16 (5)(Suppl.): Page S. (42th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, July 28-31, 2021).
- Higa S, Lin YJ, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Chiang CH, Lo MT, Chen SA. Electrophysiologically guided additional ablation after cryoballoon-based pulmonary vein isolation in patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation using PRISM index. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 16 (5)(Suppl.): Page S. (42th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, July 28-31, 2021).
- Takemoto M, Warita S, Mine T, Sakagami S, Asano T, Takei A, Suzuki M, Higa S, Miura F, Okano Y, Tao C, Kaneko S. (2019). Impact of high-density grid style catheter wave mapping on ablation strategy in de novo and redo paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Arrhythmia. 2019; Vol. 35 (10)(Suppl.): Page. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Liu CM, Lin FJ, Chen YC, Lin YK, Lu YY, Wu CI, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ. (2019) Concordant increase of post-pacing action potential duration and contractility predicts occurrence of ventricular arrhythmia in Brugada syndrome model. J Arrhythmia. 2019; Vol. 35(10)(Suppl.): Page. (12th Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Session in conjunction with 15th Asia-Pacific Atrial Fibrillation Symposium in Bangkok, Thailand, October 24-27, 2019).
- Kuo MJ, Lin YJ, Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Lo MT, Chiang CH, Chang SL, Lo LW, Hu YF, Chung FP, Lin CY, Chang TY, Liu SH, Cheng WH, Liu CM, Kuo L, Chen SA. Electrophysiologically guided pulmonary vein isolation and substrate in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation using PRISM index: a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 16 (5)(Suppl.): Page S. (42th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, July 28-31, 2021).
- Higa S, Lin YJ, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Chiang CH, Lo MT, Chen SA. Electrophysiologically guided additional ablation after cryoballoon-based pulmonary vein isolation in patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation using PRISM index. Heart Rhythm. Vol. 16 (5)(Suppl.): Page S. (42th Annual Scientific Sessions of Heart Rhythm Society in Boston, MA, USA, July 28-31, 2021).
● Book Chapters in Japan

「よくわかる臨床心臓電気生理」沖重薫(編) (2006) 中外医学社, 東京
比嘉聡
- 入門コースー薬理学的除神経とは?46-48項
- 入門コース2束ブロックとは? 57-59項
- 入門コース3束ブロックとは? 60-62項
- 基礎コースー異常自動能とは? 83-85項
- 基礎コースー心房細胞の粗動化について. 125-128項
- 発展コースー縦解離とは? 184-191項
- 応用コースー失神の症例をどう見るか? 195-199項

「よくわかる臨床心臓電気生理 改定第二版」沖重薫(編) (2008) 中外医学社, 東京
比嘉聡
- 入門コースー使用機材説明.4-10項
- 入門コースー薬理学的除神経とは? 50-52項
- 入門コース2束ブロックとは? 61-63項
- 入門コース3束ブロックとは? 64-66項
- 基礎コースー異常自動能とは? 86-88項
- 基礎コースー心房細胞の粗動化について. 128-131項
- 発展コースー縦解離とは? 188-191項
- 応用コースー失神の症例をどう見るか? 199-203項

「心房細動アブレーションを究める」山根禎一(編) (2009) メジカルビュー社, 東京
比嘉聡
- Ⅳ.Ablation Strategies.著名施設のアブレーションストラテジー、琉球大学:EnSite-guide心房細動アブレーション.222-232項
「心血管インターベンションエキスパート:カテーテルアブレーション実践テクニック」 山根禎一/夛田 浩(編) (2009) メジカルビュー社, 東京
比嘉聡
- Ⅳ.心房細動:5心房細動カテーテルアブレーション:Non-PV fociアブレーション. 156-162項